We continue the posts dedicated to design for 3D printing by looking at what a Slicer is and why it plays a fundamental role in 3D printing.
In previous posts, we had seen a basic introduction guide, 3D drawing software, and an overview of the CAD software available for creating our 3D designs.
We had left off with, one way or another, having a triangulated file in STL format with the geometry we wanted to print.
But we had also said that our printer is “dumb” and doesn’t understand 3D objects or STL formats, or anything at all. It only knows how to go to X, Y, Z coordinates and extrude a certain amount of material.
That’s precisely where the Slicer (or “slicer”) comes into play. The Slicer calculates the intersections of the 3D object with the planes at the layer height of printing and determines the resulting cross-sections. It divides it into “slices,” hence its name.
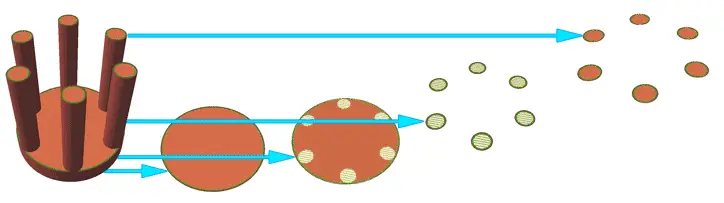
For each of these sections, it calculates the movements the print head must make to fill each area. It’s as simple and as complex as that. In a way, the Slicer is the equivalent of the “CAM program” for traditional CNC machines.
To do its job, the Slicer takes into account a large number of parameters. Speed, temperature, machine parameters, maximum dimensions, and material parameters.
Therefore, with the Slicer, we convert the 3D model in STL to the G-Code file (which we will see in the next post) that contains all the “programming” the machine will execute.
It is evident that the role of the Slicer is fundamental in the 3D printing process. First, obviously, because without it we couldn’t print. But also, the quality of the final print depends on the processing done by the Slicer.
Of course, there are a large number of Slicers available, many of them free or even Open Source. Let’s look at some of the main Slicers available.
Slicer Options
Let’s look at three great Slicer options for 3D printing. The most common is to start with Cura, which has become the de facto standard.
But it’s not the only option available. On the contrary, there are many Slicers available. Many of them are Open Source, and some are very, very good.
Ultimaker Cura
The powerful and very popular Cura is undoubtedly the benchmark to beat. Developed by Ultimaker, Cura is Open Source and compatible with a wide range of consumer printers.
Cura stands out for being suitable for both novice users and the most experienced ones. Version after version, Cura shows significant evolution in both new features and user interface.
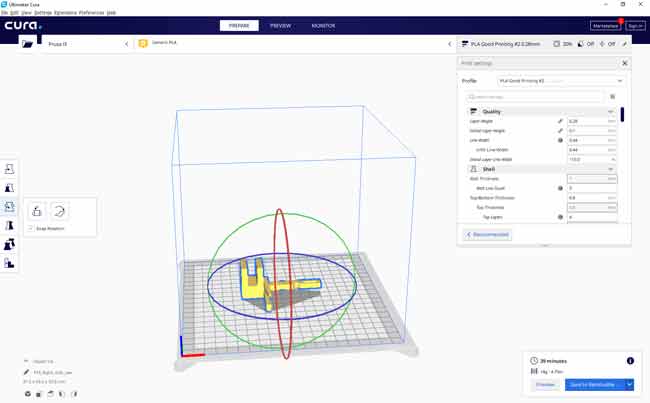
In general, the work it does is quite good, as is the print quality. It also accurately estimates print times without too much deviation.
Undoubtedly, your first option as a Slicer and an almost essential program for 3D printing.
Slic3r
Slic3r is another free Slicer program widely used in the #Maker community. Some users think Slic3r has a clearer interface with more options than Cura (or at least better organized).
Although Cura has evolved version after version, so this advantage may not be as clear, it remains one of the community’s favorite Slicers.
IdeaMaker
We finish our options with IdeaMaker, a free Slicer from Raise3D, with less diffusion than the previous ones.
Although less known, IdeaMaker has some advanced functions and generally provides very good results in both time and quality.