New entry in our 3D design and printing section, and the last in this series dedicated to getting to know the components of an FFF 3D printer in detail, which this time we will dedicate to the extruder.
We have already seen the main components of an FFF 3D printer and the parts that make it up. We have also seen in detail the extrusion head and the hotend. Now it’s time to look at the extruder, which as we have seen is the element responsible for introducing the filament into the hotend in a controlled manner.
We already saw that, depending on whether the printer is of direct drive or bowden type, the extruder will be located, respectively, on the extrusion head itself or on the frame.
Regardless of its position, the behavior and composition of the extruder is similar. The only difference is that, in the case of bowden printers, the filament will reach the hotend through a longer tube.
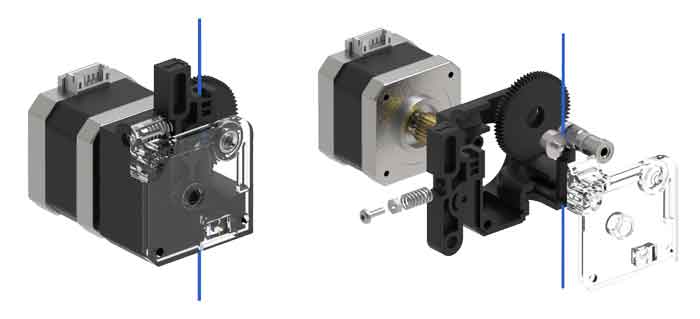
Basically, the extruder consists of a Nema 17 stepper motor, and a series of gears and wheels that are responsible for “grabbing” the filament and feeding it in. Typically, the filament is trapped between a smooth bearing and a toothed wheel. When the toothed wheel rotates, it moves the filament.
For the assembly to work correctly, the gripping pressure on the filament must be adequate. For this, there is usually some type of mechanism with a spring, whose force is controlled, for example by adjusting a spring.
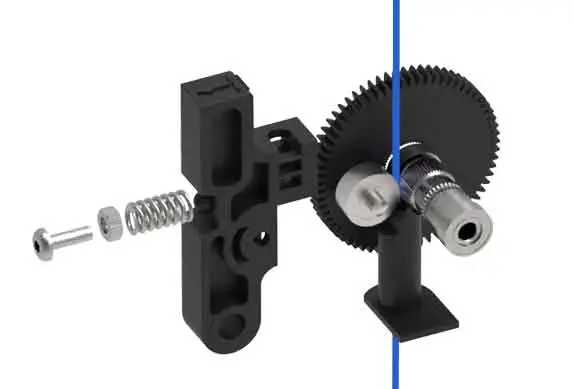
If the pressure on the filament is insufficient, it can slip and we would introduce less material than the software expects. If it is excessive, we run the risk of breaking the filament, especially when the software has to pull and push material several times (we will see this when we talk about retraction).
Regarding the motor, it has slightly different requirements than the rest of the printer. In general, it is required to have more torque. Otherwise, we risk losing steps and having an incorrect print.
Frequently, we will adjust the printer’s motor driver to allow a higher current than the rest. But that implies greater heating. Fortunately, the speeds are low, although it is possible to see some printer models that incorporate a heatsink on the extruder motor.
On the other hand, the extruder motor also needs to have greater precision (even) than the movement ones. That’s why it is also common to see motors with 400 steps per revolution, instead of the traditional 200.
Finally, in direct drive printers, the weight of the motor must be moved by the print head. In this case, it is also advisable for it to be as light as possible. Pancake-type motors, which are narrower and lighter, are often used.
For now, we have finished with this quick guide on the elements that make up an FFF 3D printer and their functionality. In the next entry of the 3D printing section, we will continue delving into this fun world by looking at 3D printing materials. See you soon!